

Med J Aust 2003 178:411.įawcett WJ, Haxby EJ, Male DA. Magnesium infusion to treat Irukandji syndrome. Anaesth Intensive Care 2001 29:552.Ĭorkeron MA. Mechanism of cardiac failure in Irukandji syndrome and first aid treatment for stings. Marine stingers: review of an under-recognized global coastal management issue. Gershwin LA, de Nardi M, Winkel KD, Fenner PJ. Australian carybdeid jellyfish causing 'Irukandji syndrome'. Tibballs J, Li R, Tibballs HA, Gershwin LA, Winkel KD.

Records of the Western Australian Museum 2014 29:10-9. Two new species of box jellies (Cnidaria: Cubozoa: Carybdeida) from the central coast of Western Australia, both presumed to cause Irukandji syndrome.
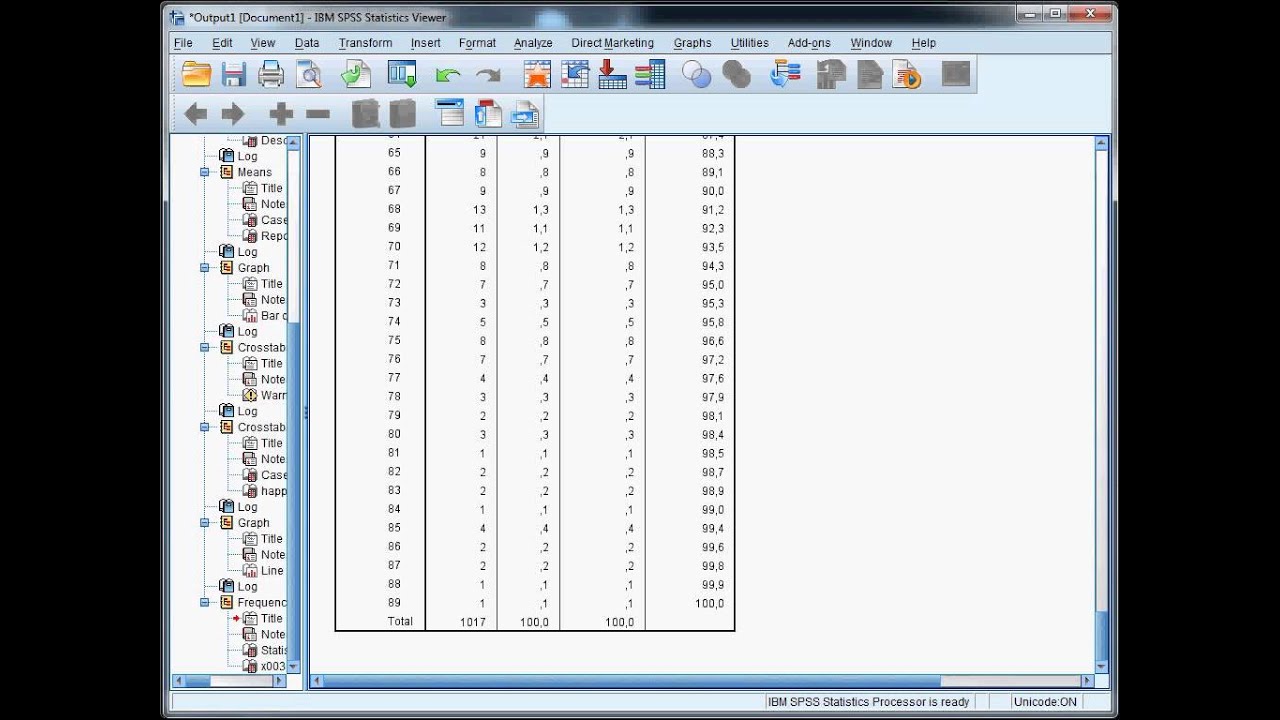
Biology and ecology of Irukandji jellyfish (Cnidaria: Cubozoa). Gershwin L, Richardson AJ, Winkel KD, et al. This study suggests that the combination of morphine and magnesium is more effective in treating patients with IS than morphine alone. There has been considerable difference of opinion as to the utility of magnesium in IS and a marked difference in the results of case series versus a small randomised control trial. Of the 54 cases in the magnesium group, 32 were normotensive post-treatment compared to only six from the morphine group (n=17). There was a lower frequency of patients in the magnesium group who remained hypertensive on arrival at a medical facility, with a significant difference between mean arterial BP of 101 mmHg (95% CI: 96–105 p=.028) and diastolic BP of 84 mmHg (95% CI: 80–88 p=.029) post-treatment. Pain reduction was statistically different (F=29.18 p<.01), between the morphine group and the magnesium group with mean numerical pain scores post-treatment of 4.91 (95% CI: 4.02–5.81) and 2.21 (95% CI: 1.66–2.76) respectively. Analyses in IBM SPSS v.22 was undertaken to determine the outcome in final pain scores and blood pressure between the two groups. A search of the QAS electronic data base found 112 patients had IS. The aim of this study was to compare pain scores and hypertensive (systolic BP ≥140 mmHg and/or diastolic BP ≥90 mmHg) patients who received intravenous morphine as their treatment (morphine group) over those who received a combination of intravenous morphine and magnesium (magnesium group).Ī retrospective case review of all IS patients attended by the QAS between 20. In 2006, the Queensland Ambulance Service (QAS) approved the use of magnesium sulphate for the management of patients with Irukandji syndrome (IS).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
